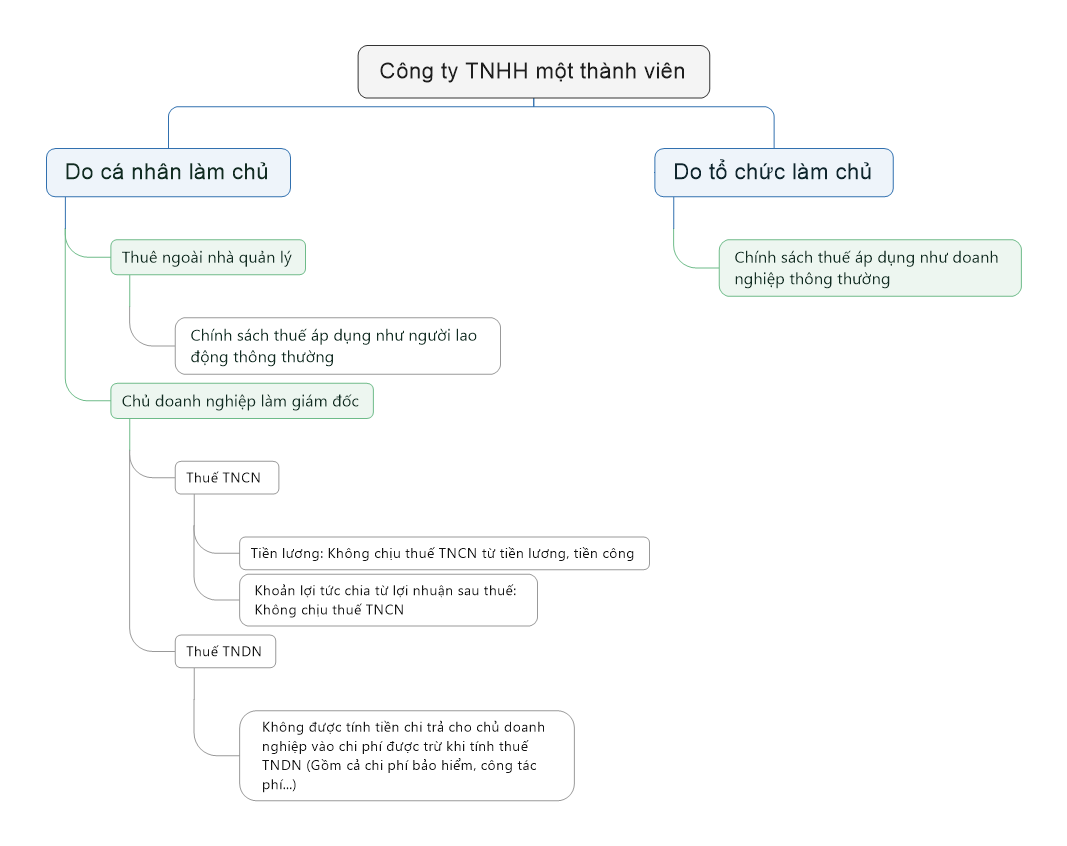
Công ty TNHH một thành viên (MTV) là một loại hình doanh nghiệp khá phổ biến ở Việt Nam. Vậy, trong trường hợp khi thành lập công ty TNHH MTV do một cá nhân làm chủ thì chủ công ty TNHH MTV (do một cá nhân làm chủ) có phải là người lao động hay không? Thu nhập mà doanh nghiệp trả cho cá nhân có phải là thu nhập từ tiền lương, tiền công không? Chính sách thuế TNDN và TNCN đối với khoản này như thế nào, bài viết dưới đây sẽ làm rõ vấn đề này.
Căn cứ pháp lý
(1) Về thuế TNCN:
– Theo Khoản 2, Điều 2, Thông tư 111/2013/TT-BTC về các khoản thu nhập chịu thuế
“…. 2.Thu nhập từ tiền lương, tiền công
Thu nhập từ tiền lương, tiền công là thu nhập người lao động nhận được từ người sử dụng lao động, bao gồm:
a) Tiền lương, tiền công và các khoản có tính chất tiền lương, tiền công dưới các hình thức bằng tiền hoặc không bằng tiền.
b) Các khoản phụ cấp, trợ cấp…”
– Tại Khoản 4 điều 2, Nghị định số 12/2015/NĐ-CP ngày 12/2/2015 của chính phủ quy định các khoản TN chịu thuế như sau:
“3. Thu nhập từ đầu tư vốn, bao gồm:
…c) Thu nhập từ đầu tư vốn dưới các hình thức khác, kể cả trường hợp góp vốn đầu tư bằng hiện vật, danh tiếng, quyền sử dụng đất, phát minh, sáng chế; trừ thu nhập nhận được từ lãi trái phiếu Chính phủ, thu nhập sau khi đã nộp thuế thu nhập doanh nghiệp của doanh nghiệp tư nhân và của công ty trách nhiệm hữu hạn một thành viên do cá nhân làm chủ.”
– Công văn 1590/TCT-CS của Tổng cục thuế ngày 22/4/2019:
Như vậy, khoản tiền của Giám đốc Công ty TNHH MTV do một cá nhân làm chủ nhận được do chính công ty chi trả không phải là thu nhập từ tiền lương, tiền công và không chịu thuế TNCN từ tiền lương tiền công.
Trường hợp chủ công ty TNHH MTV (do một cá nhân làm chủ) không phải là người đại diện theo pháp luật hay giám đốc mà ký hợp đồng lao động làm việc tại công ty và nhận lương đối với công việc đó thì họ là người lao động. Khi đó, khoản thu nhập tương ứng với công việc quy định trong hợp đồng lao động mà chủ công ty TNHH MTV (do một cá nhân làm chủ) nhận được là khoản tiền lương, tiền công và chịu thuế TNCN từ tiền lương, tiền công.
(2) Về thuế TNDN:
– Theo hướng dẫn tại điều 4 Thông tư 96/2015/TT-BTC:
“Các khoản chi không được trừ khi xác định thu nhập chịu thuế bao gồm:
…d) Tiền lương, tiền công của chủ doanh nghiệp tư nhân, chủ công ty trách nhiệm hữu hạn một thành viên (do một cá nhân làm chủ); thù lao trả cho các sáng lập viên, thành viên của hội đồng thành viên, hội đồng quản trị mà những người này không trực tiếp tham gia điều hành sản xuất, kinh doanh.”
– Công văn 142/CT-TTHT của Cục thuế tỉnh Long An ngày 18 tháng 1 năm 2018:
– Công văn 1294/CT-TTHT của Cục thuế tỉnh Bắc Giang ngày 01 tháng 04 năm 2019:
– Công văn 4729/CT-TTHT của Cục thuế tỉnh Hưng Yên ngày 9 tháng 8 năm 2018:
[spoiler title=’English version’ style=’default’ collapse_link=’true’]
Income from salaries and wages is the income that employees receive from employers. Is the owner of a limited liability company (owned by an individual) an employee? The income that business pay them is income from wages and wages and how is this income taxable, the following article will clarify this issue.
Taxes applied for income from salary and wages of the owner of a limited liability company owned by an individual:
(1) PIT
According to Clause 2, Article 2, Circular 111/2013/TT-BTC:
“Article 2. Taxable incomes
….2. Income from salary and wages
Income from salaries and wages is the income that employees receive from employers, including:
a) Salaries, wages and other items of salary or wage nature in the form of money or not in cash.
b) Allowances and subsidies, except for the following allowances and allowances:
… ”
According to the above regulation, the amount of money that the Director of a Limited Liability Company, owned by an individual, paid by the director himself is not income from salary, wages and is not subject to personal income tax.
If the owner of a limited liability company (owned by an individual) is not a legal representative or a director but signs a labor contract to work at the company and receives a salary for that job, they are workers.
Meanwhile, the income corresponding to the job specified in the labor contract that the owner of a limited liability company (owned by an individual) receives is the salary, wages and personal income tax from salary, money. public.
(2) CIT:
– According to Item d, Point 2.5, Clause 2, Article 6 of Circular 78/2014/TT-BTC:
“Expenses not deducted when determining taxable income include:
…d) Salaries and wages of owners of private enterprises, owners of one-member limited liability companies (owned by an individual); remuneration paid to the founders, members of the board of members, and the board of directors who are not directly involved in the operation of production and business. ”
– In Clause 4, Article 2, Decree No. 12/2015/ND-CP dated February 12th, 2015 of the Government stipulates that the experiments are taxable as follows:
“3. Income from capital investment, including:
…c) Income from capital investment in other forms, including in-kind investment, reputation, land use rights, inventions and inventions; except for income received from Government bond interests and income after paying corporate income tax of private enterprises and one-member limited liability companies owned by individuals. ”
Whereby:
Wages, wages, health insurance, social insurance, unemployment insurance of the owner of a limited liability company (owned by an individual), (regardless whether or not they directly participate in the management of production and business) will not be include deductible expenses when calculating CIT.
– The case of an enterprise in Vietnam is a limited liability company owned by a foreign organization that pays salaries to the director. however, the investor of this organization in foreign countries is the same person:
According to point 2.6, clause 2, article 4, TT96/2015/TT-BTC regulating non-deductible expenses when determining taxable income:
“2.6. Payment of salaries, wages and bonuses to laborers falling into one of the following cases:
…
In case Vietnamese enterprises sign contracts with foreign enterprises, stating that Vietnamese enterprises must bear the costs of accommodation for foreign experts during their working time in Vietnam, the rent for the enterprises Foreign experts working in Vietnam paid by Vietnamese enterprises shall be charged to deductible expenses when determining incomes subject to enterprise income tax. ”
In this case, salary costs and salary-related expenses for that employer will be included in deductible expenses when calculating CIT if the agreement between the overseas parent company and the company at Vietnam has regulations that companies in Vietnam must bear the costs of salaries and other expenses of the nature of salaries and wages for these employees during their working time in Vietnam and between companies in Vietnam. and the dispatched employee has signed a labor agreement as prescribed.
[/spoiler]
Biên soạn: Hoàng Thị Huệ – Tư vấn viên
Bản tin này chỉ mang tính chất tham khảo, không phải ý kiến tư vấn cụ thể cho bất kì trường hợp nào.
Để biết thêm thông tin cụ thể, xin vui lòng liên hệ với các chuyên viên tư vấn.
Đăng kí để nhận bản tin từ Gonnapass